Knights often served as vassals during the Middle Ages. The Church in the Middle Ages 2.
After the rank of king the hierarchy was the nobles the knights the clergy religious people the tradesmen and the peasants.

Church hierarchy middle ages. The Church The Roman Catholic Church grew in importance after Roman authority declined. Church in the Early Middle Ages 1. The Church influenced literature and architecture.
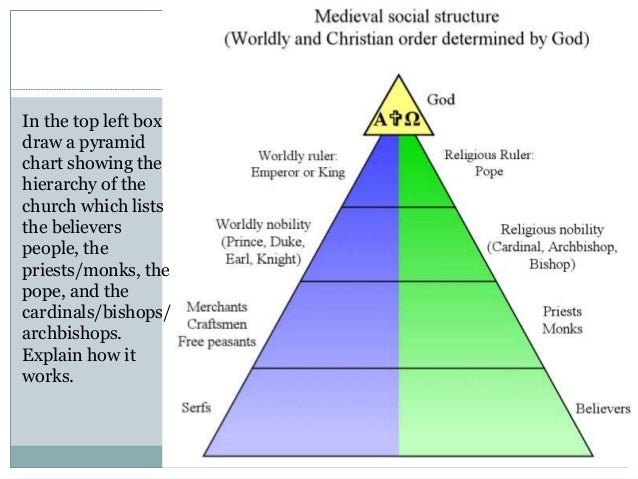
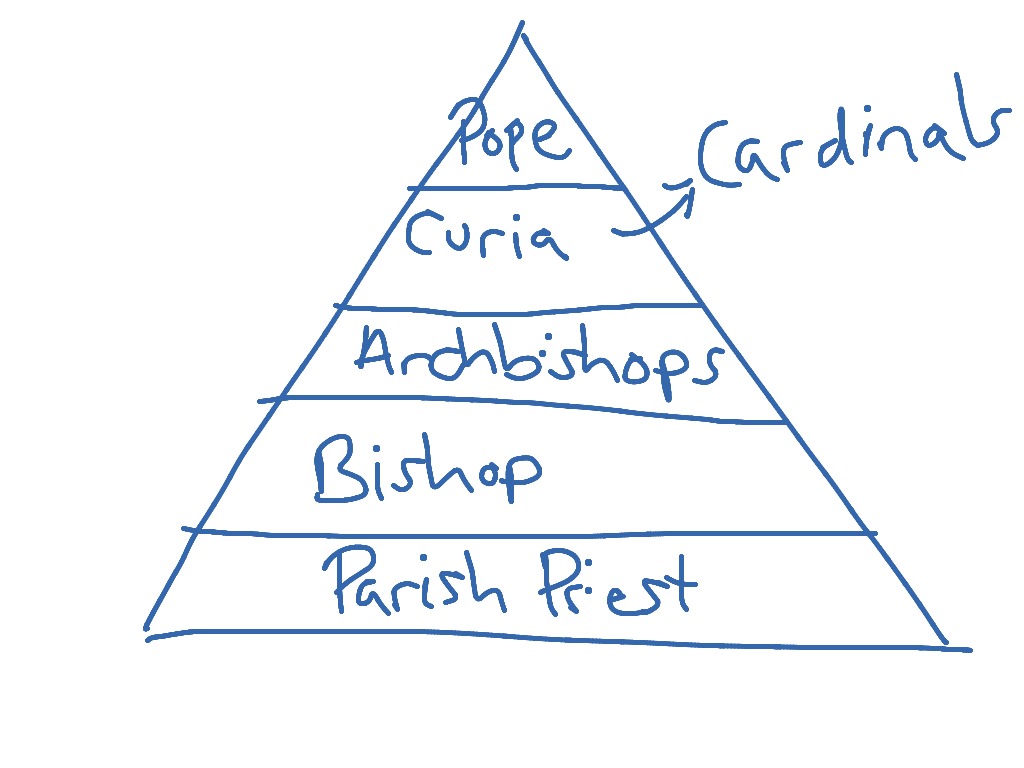
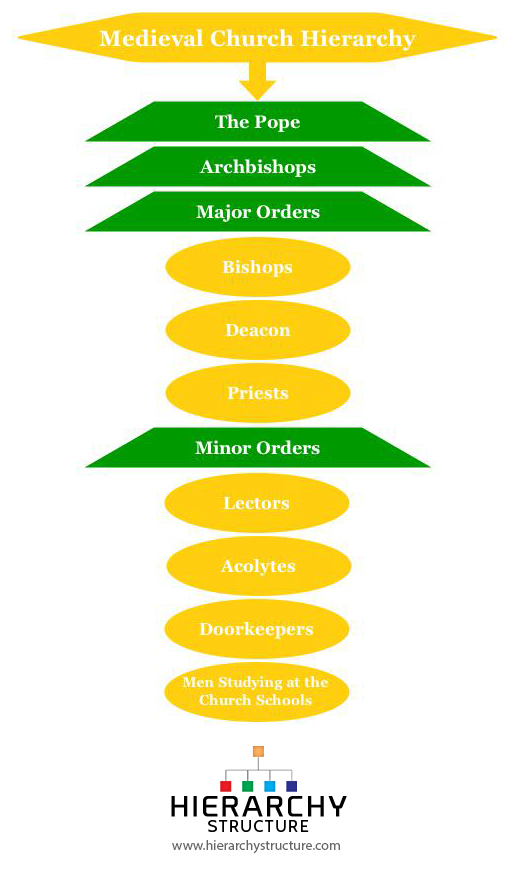
The Church One of the most unifying elements of the Middle Ages was the Roman Catholic Church. The hierarchy of the Catholic Church consists of its bishops priests and deacons. Administrators of the Church BishopsArchbishops ecclesiastical superiors over a cathedral or region Priests ecclesiastical authorities over a parish village.
In canonical and general usage it refers to those who exercise authority within a Christian church. At the head of the church was the Pope who was advised by the cardinals. Popes have a heavy influence over political and economical decisions for a long time.
The middle ages were a turbulent time marked by wars in which millions of lives were lost. Early Middle Ages Hierarchy of the Church 9-3 The Church The Church was well established by the fall of the Western Roman Empire 476 AD. When the WRE collapsed the church survived.
By copying ancient books and manuscripts the monks helped preserve Greco-Roman culture. The church in the middle ages played a central role in peoples lives as well as the state. The Pope was the most powerful figure in the Church hierarchy.
The Medieval Catholic Church was and still is organized according to a strict hierarchy. The church was a universal all encompassing institution with the Roman Catholic. The population of one of these villages often did not exceed 100 people.
There is a set hierarchy in the Roman Catholic Church which has many levels Starting from the bottom this is the order. The church played a strong and controversial role during these tumultuous times. It is the larges and most important unifying factor to survive in Western Europe.
By the time of the Middle Ages the Church had an established hierarchy. People gave the church 110th of their earnings in tithes. The body of religious worshipers as distinguished from the clergy.
For much of the Middle Ages Popes had the last say in anything to do with the church. They also paid the church for various sacraments such as baptism marriage and communion. People also paid penances to the church.
The Church hierarchy was Pope then the cardinals archbishops bishops and abbots and priests monks and nuns. The Catholic Church became very rich and powerful during the Middle Ages. While the feudalism and social structure of the middle ages varied drastically from manor to manor and while there were constantly fluctuating customs in response to different situations there was a consistent theme throughout enforcing a strict and organized hierarchy defined as an age of Feudalism.
In the ecclesiological sense of the term hierarchy strictly means the holy ordering of the Church the Body of Christ so to respect the diversity of gifts and ministries necessary for genuine unity. It became the unifying force in western Europe. The only important buildings in a villages were the parish church the parsonage a mill a stream if one ran through the manor and possibly a blacksmiths shop.
Their primary duty as a vassal was to aid and to protect the lord in his army. A transitional deacon is a seminarian studying for the priesthood. Pope the head of the Church Cardinals advisors to the Pope.
Church hierarchy Although the general public was illiterate the clergy could read and write. The hierachy of the church was like everything else in the Middle Ages pyramid shaped. The Popes the Hierachy and the Inquisition The Popes in the Middle Ages had authority over the kings which gave great power to the Roman Catholic church in the Middle Ages.
The Church in the Middle Ages. There was only one pope and along with having religious responsibilities he also had political power nearly equal to the power of the monarch. Missionaries spread Christianity to the Germanic Tribes and bring with them the remains of Roman culture.
Medieval village life during the Middle Ages was self-sufficing. Medieval authors usually members of the clergy wrote about religious themes. The cardinals were in charge of the bishops each of whom were assigned to a cathedral -- usually within a city -- and oversaw the religious activities in their area such as mass and sacraments which were performed by priests.
 Church In The Early Middle Ages
Church In The Early Middle Ages
 Medieval Church Hierarchy History Medieval Europe Europe Showme
Medieval Church Hierarchy History Medieval Europe Europe Showme
 Medieval Church Hierarchy Medieval Church Structure
Medieval Church Hierarchy Medieval Church Structure
 Medieval England Vs Medieval Japan Sutori
Medieval England Vs Medieval Japan Sutori
 The Role Of The Church In The Middle
The Role Of The Church In The Middle
Social Structure Medieval Europe
 The Church 13 3 The Rise Of The Middle Ages Global 9
The Church 13 3 The Rise Of The Middle Ages Global 9
 Chapter 13 Section 3 The Church The Church And The Middle Ages Middle Ages The Church S Presence Was Felt Everywhere Throughout Europe 1100s Medieval Ppt Download
Chapter 13 Section 3 The Church The Church And The Middle Ages Middle Ages The Church S Presence Was Felt Everywhere Throughout Europe 1100s Medieval Ppt Download